10^4-10^6Ω/10^6-10^9Ω
In static-sensitive environments such as modern electronics industries, medical facilities, laboratories, and data processing centers, the choice of antistatic flooring is crucial. Many people are confused by the two resistance specifications: “10×10^4Ω—10×10^6Ω“ and “10×10^6Ω—10×10^9Ω“. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the differences between these two specifications, their applicable scenarios, and the selection criteria.
Technical differences between the two resistance specifications

10×10^4—10×10^6 ohm (10^4-10^6Ω) flooring
Resistance range: 10,000 to 1,000,000 ohms
Conductivity: High conductivity
Discharge rate: Fast electrostatic dissipation
Material characteristics: Typically contains a higher proportion of conductive filler
10×10^6—10×10^9 ohm (10^6-10^9Ω) flooring
Resistance range: 1,000,000 to 1,000,000,000 ohms
Conductivity: Medium conductivity
Discharge rate: Slow and controllable electrostatic discharge
Material characteristics: Relatively low proportion of conductive filler
Industry Standards and Specifications Based on:
According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 61340-5-1 standard and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 99 standard, antistatic flooring is divided into three categories:
Conductive: Resistance range 10^4-10^6 Ω
Static Dissipative: Resistance range 10^6-10^9 Ω
Antistatic: Resistance higher than 10^9 Ω
Similar classifications are also adopted in European standard EN 1081 and domestic standard GB/T 26539-2011.
Application Scenarios Selection
Locations requiring 10^4-10^6Ω flooring :
Electronics manufacturing and assembly workshops
Semiconductor production lines
Microelectronics assembly areas
Integrated circuit testing areas
Explosive and flammable environments
Hospital operating rooms (especially when using flammable anesthetics)
Chemical laboratories handling flammable solvents
Petrochemical control rooms
Reason: These environments require rapid removal of static charge to prevent static buildup from igniting sparks, which could lead to explosions or damage to extremely static-sensitive microelectronic components (components with ESD sensitivity <100V).

Locations requiring 10^6-10^9Ω flooring:
Data centers and server rooms
Server rack areas
Network equipment rooms
Data storage centers
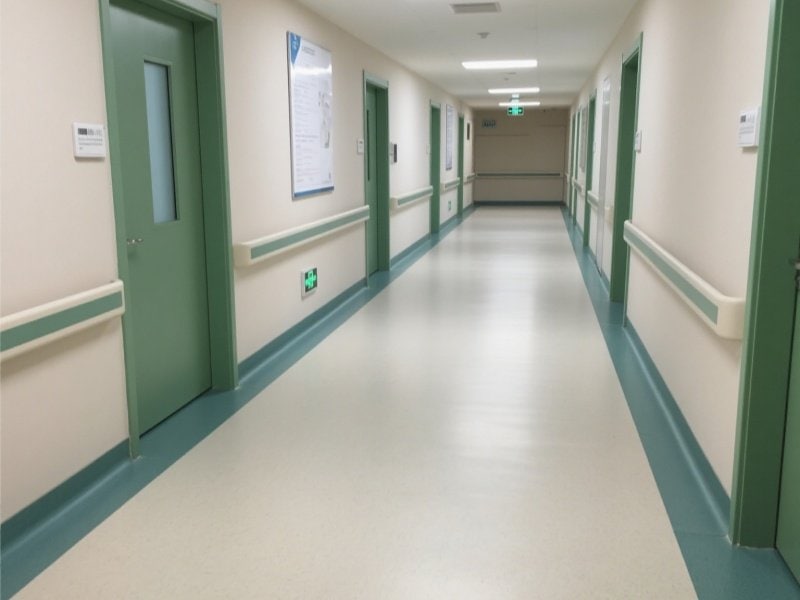
Medical diagnostic areas
Medical imaging rooms (CT, MRI, etc.)
Cardiac monitoring centers
Medical electronic equipment operating areas
General electronic work areas
Computer repair workshops
Telecommunications equipment rooms
General electronic product testing areas
Reason: These locations require controlled electrostatic discharge rates to prevent both static buildup and excessively rapid discharge current interference with the regular operation of precision electronic equipment. This is especially important for medical equipment, where excessively rapid electrostatic discharge can interfere with the monitoring of sensitive biological signals.

How to choose the resistor of anti–static flooring?

Installation and Maintenance Precautions
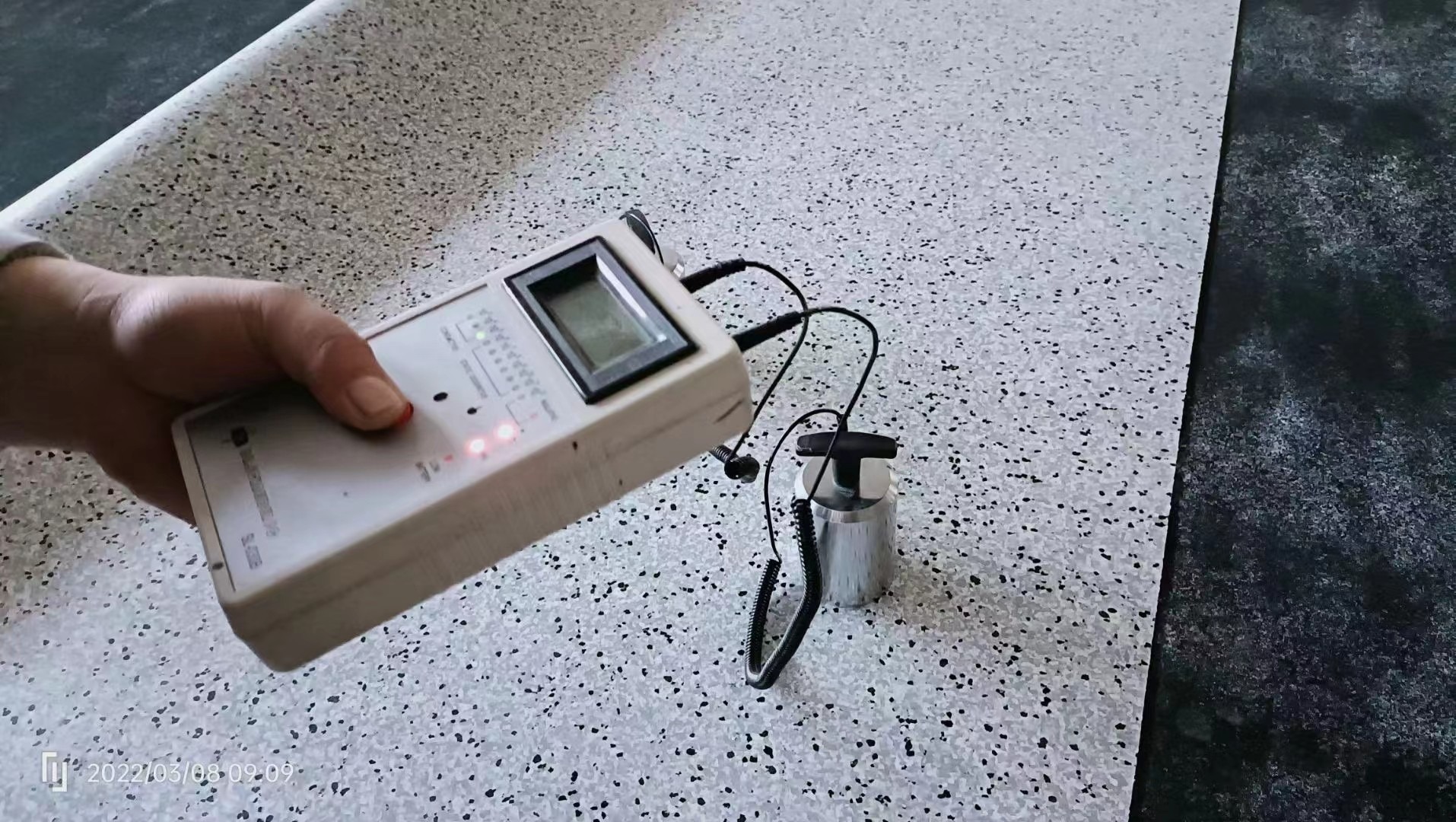
Grounding System Integrity: Regardless of the flooring type selected, a proper grounding system is essential. The grounding resistance should be less than 10Ω.
Humidity Influence: Ambient humidity should be controlled between 40% and 60% RH. Flooring resistance may increase when the humidity is below 30%.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Use a dedicated anti-static cleaner; avoid using wax-based or oil-based cleaners.
Regular Testing: Flooring resistance should be tested every six months using a resistance tester conforming to ASTM F150.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
Misconception 1: “Lower resistance is better.”
Fact: Excessively low resistance can lead to leakage current problems, interfering with sensitive electronic equipment.
Misconception 2: Two types of flooring can be used interchangeably.
Fact: Flooring with the same resistance specification should be used in the same area; otherwise, a potential difference may occur.
Misconception 3: Flooring alone can completely solve static electricity problems.
Fact: A complete electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection system includes grounding, personnel equipment (anti-static clothing, wrist straps), environmental control, and equipment grounding.
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate resistance specification for antistatic homogeneous PVC flooring is not a simple matter of choosing one of two options; rather, it requires careful consideration of site characteristics, equipment sensitivity, safety requirements, and the usage environment. Flooring with a resistance of 10^4-10^6 Ω is suitable for high-risk electrostatic hazard environments, while flooring with a resistance of 10^6-10^9 Ω is suitable for most electronic equipment and medical settings. The correct selection not only protects equipment but also ensures personnel safety and reduces economic losses caused by static electricity.
It is recommended to consult with an antistatic engineer during the project planning phase and refer to the latest industry standards for design and selection to ensure the effectiveness and compliance of the electrostatic protection system. Learn more…….